Denver Developmental Screening Test Training Manual
Posted by admin- in Home -19/11/17 GDS by Medical dictionary. L. scala, staircase 1. A graduated or proportioned measure. A tool that rates people, places, or things in relation to one another. A scale used for indicating low temperatures based on absolute zero. It is used in thermodynamic calculations of, for example, heatenergy transfer. Synonym Kelvin scale See absolute temperature absolute zero.
GDS by Medical dictionary. L. scala, staircase 1. A graduated or proportioned measure. A tool that rates people, places, or things in relation to one another. A scale used for indicating low temperatures based on absolute zero. It is used in thermodynamic calculations of, for example, heatenergy transfer. Synonym Kelvin scale See absolute temperature absolute zero. 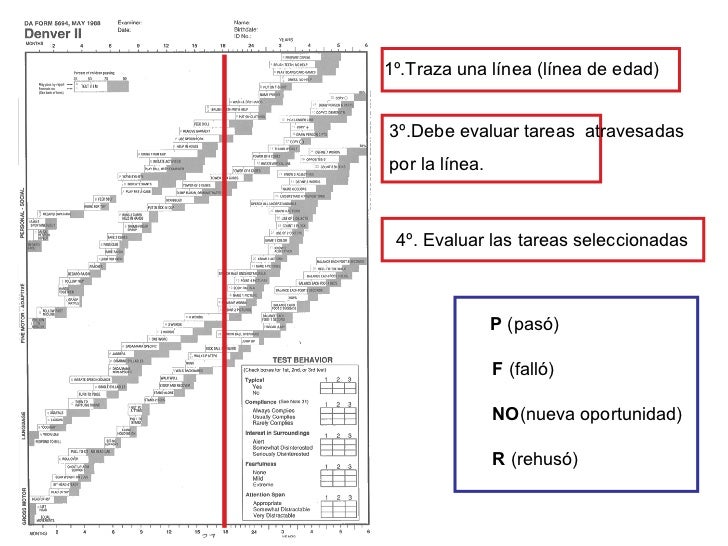 In the United States, a revision to autism spectrum disorder ASD was presented in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders version 5, released May. Activities Specific Balance Confidence Scale Abbreviation ABCA 1. ADLs without losing balance and falling.
In the United States, a revision to autism spectrum disorder ASD was presented in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders version 5, released May. Activities Specific Balance Confidence Scale Abbreviation ABCA 1. ADLs without losing balance and falling.  The patient ranks his confidence to complete each item from 0 no confidence to 1. ASIA Impairment Scale. A method of assessing the degree of motor and sensory impairment in spinal cord injured patients. The assessment is based on an examination of the perineum and anus, i. S4 S5 level of the spinal cord. Grade A Complete No motor or sensory function Grade B Incomplete, sensory function is intact, but motor function is absent below and including the S4 S5 level Grade C Incomplete, motor function is preserved below the neurological level and more than half of the primary muscles have a muscle grade test of less than 3 Grade D Incomplete Motor function is preserved and at least half of the muscles below the S4 S5 level have a muscle grade test of 3 or better and Grade E Normal. Borg dyspnea scale See Borg dyspnea scale. Braden scale See Braden scale. Brazelton Neonatal Assessment Scale See Brazelton Neonatal Assessment Scale. Celsius scale See Celsius, Anderscentigrade scale. Celsius scale. See Celsius, Anders. Clinical Linguistic and Auditory Milestone Scale Abbreviation CLAMSAn office test used to evaluate language development in children from birth to age 3. See Denver Developmental Screening Testscale of contrast. The range of densities on a radiograph the number of tonal grays that are visible. Disability Rating Scale. An instrument to gauge the functional capabilities and progress of a person with moderate to severe brain injury. A person who has no deficits after recovery from brain injury receives a score of 0 not impaired. A severely impaired person who is unemployable, unable to care for himself, and unable to open his eyes, move, or speak receives the lowest score 2. Fahrenheit scale See Fahrenheit, Daniel Gabriel. Falls Efficacy Scale, falls efficacy scale Abbreviation FESA questionnaire to assess the level of confidence that patients have in performing activities of daily living without fear of falling. French scale A system to indicate the diameter of catheters and sounds. Each unit on the scale is approximately equivalent to one third mm thus a 2. French sound is 7 mm in diameter. The size of the diameter of the catheter increases as the numerical value of French increases. Geriatric Depression Scale Abbreviation GDS A 3. Medicare. Glasgow Coma Scale Abbreviation GCSA scale to determine a patients level of consciousness. It is a rating from 3 to 1. The GCS is used primarily during the examination of patients with trauma or stroke. Repeated examinations can help determine if the patients brain function is improving or deteriorating. Many EMS systems use the GCS for triage purposes and for determining which patients should be intubated in the field. See tablecoma Trauma Score. Glasgow Outcome Scale. A scale that assesses current neurological awareness of the environment, and recovery and disability in all types of brain injury. Nutrition Plans for Morning Workouts. Working out in the morning gives you an energy boost and ensures that you get your workout done before your schedule gets in the. Fake News Papers Fake News Videos. A Few Abbreviations. The scale is to be used during the evaluation of trauma, stupor, or coma, and at prescribed time intervals, such as 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year after injury. The Glasgow group reports the greatest recovery in the 6 month period after injury. The nurse or other health care practitioner notes the patients abilities at a particular time using this practical scale Good outcome may have minimal disabling sequelae but returns to independent functioning comparable to preinjury level and a full time job Moderate disability is capable of independent functioning but not of returning to full time employment Moderate disability is capable of independent functioning but not of returning to full time employment Severe disability depends on others for some aspect of daily living Persistive vegetative state has no obvious cortical functioning Dead. Global Assessment of Functioning Scale Abbreviation GAF scale. A scale that rates a persons social, occupational, and psychological functioning. The scale rates from high functioning, i. There is a childrens version of the scale, called the Childrens Global Assessment of Functioning CGAF. Global Assessment of Relational Functioning Scale Abbreviation GARF scale. A measure of the degree to which a family meets the emotional and functional needs of its members. A scale used to express the degree of acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The classic p. H scale extends from 0. H concentration. The p. H value is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion p. H concentration of a solution, expressed in moles per liter. As the hydrogen ion concentration decreases, a change of 1 p. H unit means a 1. Thus a solution with a p. H of 1. 0 is 1. 0 times more acid than one with a p. H of 2. 0 and 1. 00 times more acid than one with a p. H of 3. 0. A p. H of 7. Very concentrated 1molar mineral acids and bases go beyond the classic scale to values lt 0. As the hydrogen ion concentration varies in a definite reciprocal manner with the hydroxyl ion OH concentration, a p. H reading above 7. In the human body, arterial blood is slightly alkaline, having a normal p. H range of 7. 3. 5 to 7. See p. HKarnofsky Scale. Karnofsky Index. Kelvin scale See Kelvin, Lord. Klein Bell ADL Scale See Klein Bell ADL Scale. Kurtzke Expanded Disability Status Scale See Kurtzke Expanded Disability Status Scale. Morse Falls Scale See Morse Falls Scale. Motor Assessment Scale. An eight item measurement tool used to assess motor function and physical mobility after a stroke. Norton scale See Norton scale. Nottingham Extended Activities of Daily Living Scale. A widely used European scale of a persons activities of daily living that measures mobility and the ability to function in domestic tasks, kitchen tasks, and leisure activities. See instrumental activities of daily living. Oswestry Disability Scale. Oswestry Disability Index. An assessment tool used to measure the intensity of a patients discomfort. See Numerical Rating Scale visual analog scale. Norton scale See Norton scale. Numerical Rating Scale, Numeric Rating Scale. Abbreviation NRSA variation of the visual analog scale that uses a scalar numbering system to objectify a patients pain. Most numeric rating scales use a 1. The leftmost mark is labeled 0 and has the notation No Pain. The rightmost mark is labeled 1. Worst pain imaginable. The patient is asked to indicate where on the continuum he or she would rate the current intensity of pain. Abbreviation RBRVSA scale for determining the monetary value of evaluation and management services provided to patients, i. The scale is based on the total work required for a given service and on other considerations, including the cost of the physicians practice, the income lost during training, and the relative cost of liability insurance. See managed care managed competition. Stroke Impact Scale. An instrument to measure the effect of a stroke on a persons mobility, speech, social activities, manual dexterity, strength, emotions, memory, and daily activities. Vancouver scar scale. Burn scar index. visual analog scale.
The patient ranks his confidence to complete each item from 0 no confidence to 1. ASIA Impairment Scale. A method of assessing the degree of motor and sensory impairment in spinal cord injured patients. The assessment is based on an examination of the perineum and anus, i. S4 S5 level of the spinal cord. Grade A Complete No motor or sensory function Grade B Incomplete, sensory function is intact, but motor function is absent below and including the S4 S5 level Grade C Incomplete, motor function is preserved below the neurological level and more than half of the primary muscles have a muscle grade test of less than 3 Grade D Incomplete Motor function is preserved and at least half of the muscles below the S4 S5 level have a muscle grade test of 3 or better and Grade E Normal. Borg dyspnea scale See Borg dyspnea scale. Braden scale See Braden scale. Brazelton Neonatal Assessment Scale See Brazelton Neonatal Assessment Scale. Celsius scale See Celsius, Anderscentigrade scale. Celsius scale. See Celsius, Anders. Clinical Linguistic and Auditory Milestone Scale Abbreviation CLAMSAn office test used to evaluate language development in children from birth to age 3. See Denver Developmental Screening Testscale of contrast. The range of densities on a radiograph the number of tonal grays that are visible. Disability Rating Scale. An instrument to gauge the functional capabilities and progress of a person with moderate to severe brain injury. A person who has no deficits after recovery from brain injury receives a score of 0 not impaired. A severely impaired person who is unemployable, unable to care for himself, and unable to open his eyes, move, or speak receives the lowest score 2. Fahrenheit scale See Fahrenheit, Daniel Gabriel. Falls Efficacy Scale, falls efficacy scale Abbreviation FESA questionnaire to assess the level of confidence that patients have in performing activities of daily living without fear of falling. French scale A system to indicate the diameter of catheters and sounds. Each unit on the scale is approximately equivalent to one third mm thus a 2. French sound is 7 mm in diameter. The size of the diameter of the catheter increases as the numerical value of French increases. Geriatric Depression Scale Abbreviation GDS A 3. Medicare. Glasgow Coma Scale Abbreviation GCSA scale to determine a patients level of consciousness. It is a rating from 3 to 1. The GCS is used primarily during the examination of patients with trauma or stroke. Repeated examinations can help determine if the patients brain function is improving or deteriorating. Many EMS systems use the GCS for triage purposes and for determining which patients should be intubated in the field. See tablecoma Trauma Score. Glasgow Outcome Scale. A scale that assesses current neurological awareness of the environment, and recovery and disability in all types of brain injury. Nutrition Plans for Morning Workouts. Working out in the morning gives you an energy boost and ensures that you get your workout done before your schedule gets in the. Fake News Papers Fake News Videos. A Few Abbreviations. The scale is to be used during the evaluation of trauma, stupor, or coma, and at prescribed time intervals, such as 3 months, 6 months, and 1 year after injury. The Glasgow group reports the greatest recovery in the 6 month period after injury. The nurse or other health care practitioner notes the patients abilities at a particular time using this practical scale Good outcome may have minimal disabling sequelae but returns to independent functioning comparable to preinjury level and a full time job Moderate disability is capable of independent functioning but not of returning to full time employment Moderate disability is capable of independent functioning but not of returning to full time employment Severe disability depends on others for some aspect of daily living Persistive vegetative state has no obvious cortical functioning Dead. Global Assessment of Functioning Scale Abbreviation GAF scale. A scale that rates a persons social, occupational, and psychological functioning. The scale rates from high functioning, i. There is a childrens version of the scale, called the Childrens Global Assessment of Functioning CGAF. Global Assessment of Relational Functioning Scale Abbreviation GARF scale. A measure of the degree to which a family meets the emotional and functional needs of its members. A scale used to express the degree of acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The classic p. H scale extends from 0. H concentration. The p. H value is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion p. H concentration of a solution, expressed in moles per liter. As the hydrogen ion concentration decreases, a change of 1 p. H unit means a 1. Thus a solution with a p. H of 1. 0 is 1. 0 times more acid than one with a p. H of 2. 0 and 1. 00 times more acid than one with a p. H of 3. 0. A p. H of 7. Very concentrated 1molar mineral acids and bases go beyond the classic scale to values lt 0. As the hydrogen ion concentration varies in a definite reciprocal manner with the hydroxyl ion OH concentration, a p. H reading above 7. In the human body, arterial blood is slightly alkaline, having a normal p. H range of 7. 3. 5 to 7. See p. HKarnofsky Scale. Karnofsky Index. Kelvin scale See Kelvin, Lord. Klein Bell ADL Scale See Klein Bell ADL Scale. Kurtzke Expanded Disability Status Scale See Kurtzke Expanded Disability Status Scale. Morse Falls Scale See Morse Falls Scale. Motor Assessment Scale. An eight item measurement tool used to assess motor function and physical mobility after a stroke. Norton scale See Norton scale. Nottingham Extended Activities of Daily Living Scale. A widely used European scale of a persons activities of daily living that measures mobility and the ability to function in domestic tasks, kitchen tasks, and leisure activities. See instrumental activities of daily living. Oswestry Disability Scale. Oswestry Disability Index. An assessment tool used to measure the intensity of a patients discomfort. See Numerical Rating Scale visual analog scale. Norton scale See Norton scale. Numerical Rating Scale, Numeric Rating Scale. Abbreviation NRSA variation of the visual analog scale that uses a scalar numbering system to objectify a patients pain. Most numeric rating scales use a 1. The leftmost mark is labeled 0 and has the notation No Pain. The rightmost mark is labeled 1. Worst pain imaginable. The patient is asked to indicate where on the continuum he or she would rate the current intensity of pain. Abbreviation RBRVSA scale for determining the monetary value of evaluation and management services provided to patients, i. The scale is based on the total work required for a given service and on other considerations, including the cost of the physicians practice, the income lost during training, and the relative cost of liability insurance. See managed care managed competition. Stroke Impact Scale. An instrument to measure the effect of a stroke on a persons mobility, speech, social activities, manual dexterity, strength, emotions, memory, and daily activities. Vancouver scar scale. Burn scar index. visual analog scale.